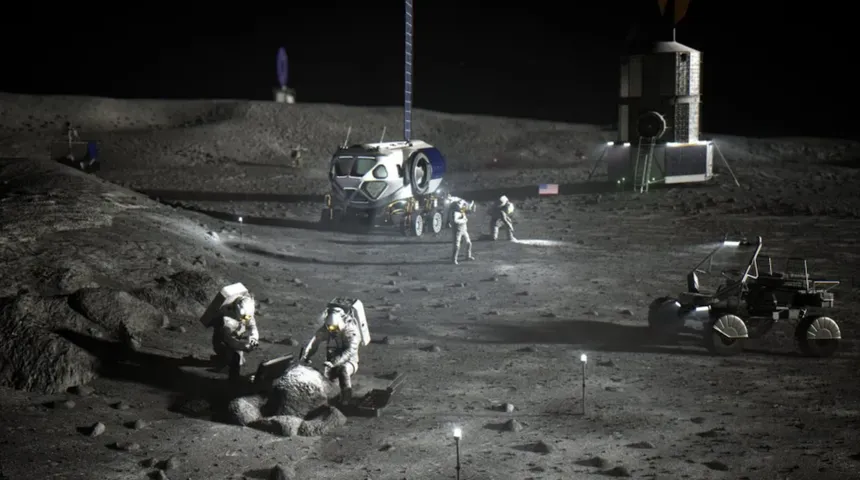
NASA is considering a novel approach to build a railway on the lunar surface that uses levitating robots to provide efficient payload transport on the moon. The space agency has proposed the Flexible Levitation on a Track (FLOAT) system, which would play a crucial role in the daily operations of an astronaut-inhabited lunar base. FLOAT would be used to move regolith mined for construction, transport payloads around the lunar base, and even to and from landing zones or exploration sites.
The FLOAT system consists of unpowered magnetic robots that levitate over a 3-layer flexible film track. The graphite layer enables robots to passively float over tracks using diamagnetic levitation, while the flex-circuit layer generates electromagnetic thrust to controllably propel robots along tracks. An optional thin-film solar panel layer generates power for the base when in sunlight. Individual FLOAT robots would be capable of transporting payloads of different shapes and sizes at speeds of up to 0.5 meters per second, and a large-scale system would be able to move up to 100,000 kilograms of material multiple kilometers per day.
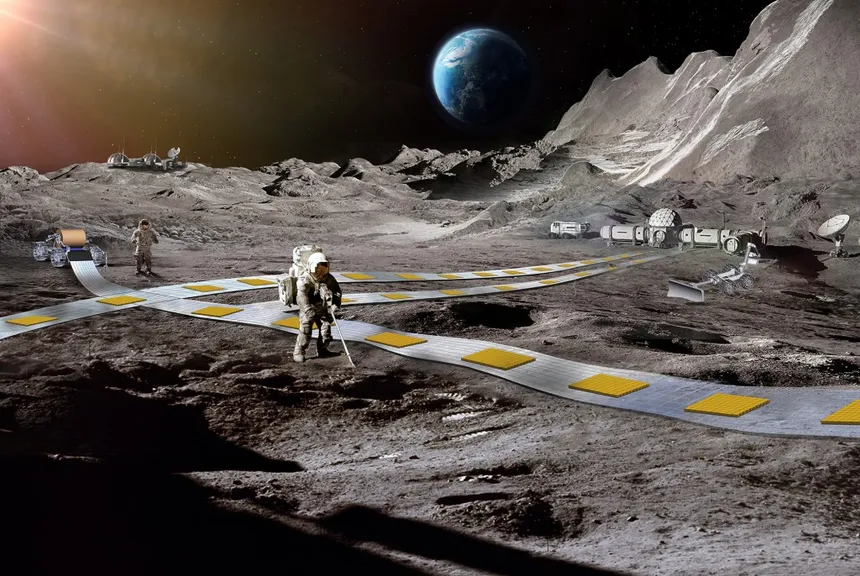
NASA Exploring Railway on Lunar Surface for Efficient Payload Transport
One of the significant advantages of the FLOAT system is its minimization of lunar dust abrasion. Since the robots have no moving parts and levitate over the track, they reduce the risk of damaging the system over time. This would require less maintenance compared to robots with wheels, legs, or tracks. The tracks would also be rolled up before being unfurled directly onto the lunar surface, eliminating the need for challenging and time-consuming construction work by astronauts.
The concept of building a railway on the lunar surface is still in its early stages, with the next step involving the construction of subscale robot and track prototypes for testing in a lunar-analog environment. This would allow for the refinement and improvement of the FLOAT design. Furthermore, systems for manufacturing the necessary hardware at scale would need to be developed.
NASA’s aim is to send astronauts back to the moon in the Artemis III mission currently set for 2026, followed by the construction of a moonbase where astronauts can live and work in a similar way to how they do on the International Space Station today. The FLOAT system has the potential to revolutionize the way payload transport is handled on the moon, providing a reliable, autonomous, and efficient way to move materials around the lunar surface.