Micron’s Crucial division has introduced two new types of memory modules: CUDIMMs for laptops and CSODIMMs for desktops. These new modules are designed to support higher memory speeds, which will be essential with the arrival of Intel’s Arrow Lake processors.
The key feature of these modules is the integration of a small clock driver circuit directly onto the module, marking a shift from traditional DIMMs that rely on the CPU’s clock for memory timing.
CUDIMMs and CSODIMMs can reach DDR5-6400 speeds, offering a performance boost of 6,400 megatransfers per second, which is approximately 15% faster than standard DDR5 DIMMs.
The onboard clock driver allows for more precise memory timing, enabling the higher speeds needed for modern applications. Without this enhancement, traditional methods would struggle to manage these faster speeds due to timing limitations.
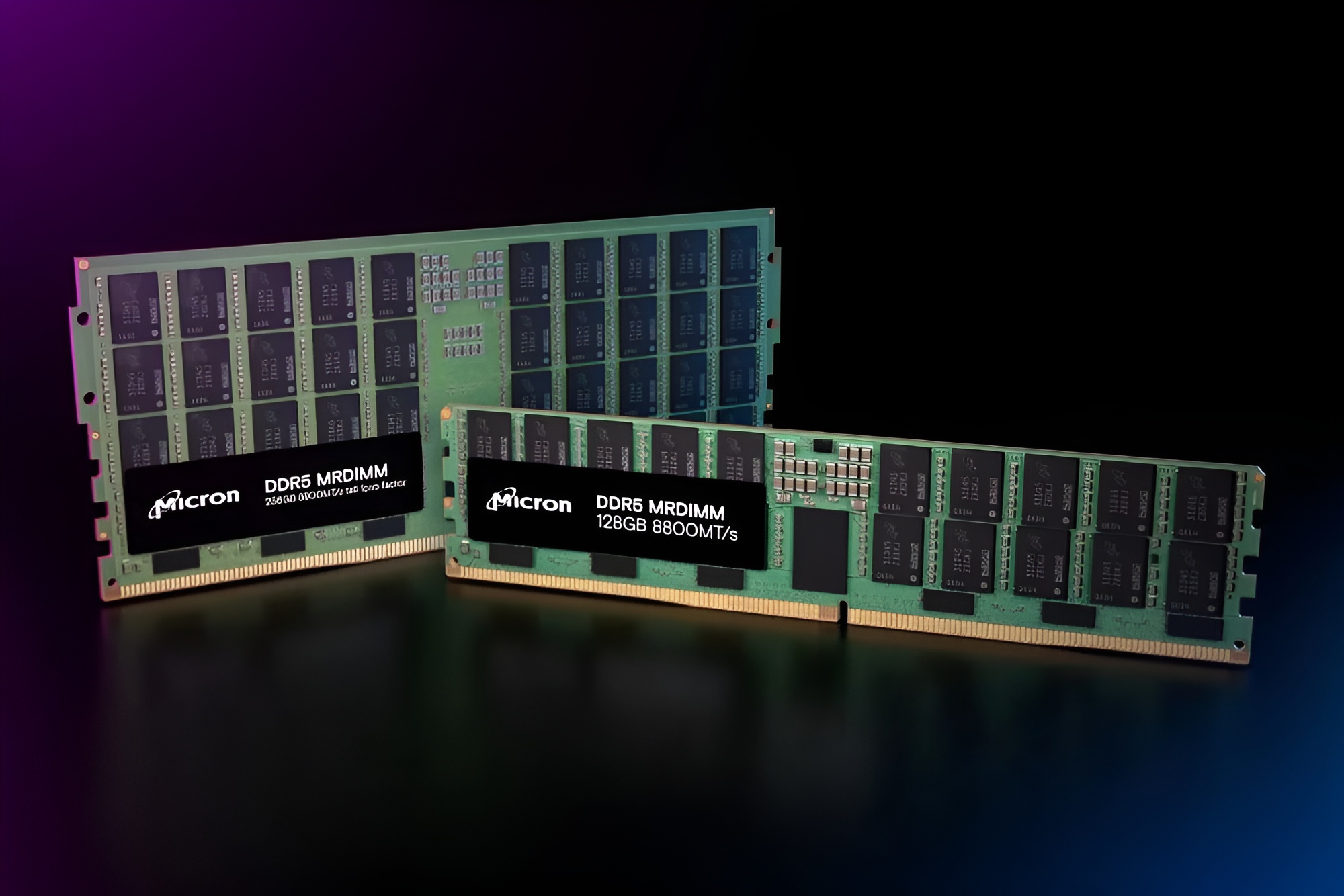
Micron’s Crucial Introduces High-Speed CUDIMMs and CSODIMMs for Next-Gen Intel Arrow Lake Systems
These new modules are versatile, catering to advanced users working with AI applications, but they also serve general-purpose needs. Gamers, for instance, can benefit from the increased memory performance for demanding tasks. The speed improvements provided by these modules will enhance a wide range of computing tasks, from running AI models to improving gaming experiences.
Intel has already validated these memory modules for use with its upcoming Arrow Lake chips, which are expected to begin shipping soon.
Micron has started delivering the new memory modules to PC manufacturers, with capacities of up to 64GB per module, allowing for a total system memory of up to 256GB. Consumer sales are expected to begin in the first half of 2025, though pricing details are yet to be disclosed. These modules will also come with a limited lifetime warranty.
It’s important to note that these CUDIMMs are distinct from another new memory technology, CAMM2. CAMM, or Compression Attached Memory Module, is specifically designed for laptops and offers a compact, upgradable memory solution.
While both technologies represent advances in memory performance, CUDIMMs and CAMM modules address different needs—CUDIMMs for high-speed, high-capacity desktop performance, and CAMMs for more portable, compact laptop memory solutions.